Pulmonary Hypertension Class 3 Treatment
Place catheter 2 ng/kg/min increased by 2. Group 4 pulmonary hypertension, or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (cteph), is the only type of pulmonary hypertension that can be cured.
Pulmonary hypertension caused by lung disease.

Pulmonary hypertension class 3 treatment. It is rare for a patient to be diagnosed while still a class i. The treatment methods keep changing depending on the effectiveness of medicines given. Pulmonary hypertension due to lung disease (group 3) this large and diverse group of diseases share in common that the primary problem is within the lungs or the control of lung function.
We believe in a future where all rare diseases are understood and treated Class i patients with pulmonary hypertension but without resulting limitations of physical activity. We believe in a future where all rare diseases are understood and treated
Pulmonary hypertension (ph) or pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) is a serious, progressive disease in which there is elevated blood pressure in the arteries supplying to the lungs. Cteph is caused by blood clots in the pulmonary arteries, and many patients are able to undergo a surgical procedure, called pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (pte) to remove these clots. 63 other agents, including bosentan, have been evaluated.
Ad let’s build the knowledge bank to better understand, talk about, and manage rare disease. Pulmonary hypertension treatment overview by functional class More often this classification is used to describe patients that have demonstrated a substantial response to therapy that were once a class ii or iii but have improved to a class i.
It often takes some time to find the most appropriate treatment for pulmonary hypertension. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) pulmonary fibrosis, a condition that causes scarring in the tissue between the lungs' air sacs (interstitium) obstructive sleep apnea; There is no cure for pulmonary hypertension, however, there are treatments recommended to ease tension from pulmonary arteries to decrease the progress of pulmonary hypertension.
When pulmonary hypertension is caused by another condition, your doctor will treat the underlying cause whenever possible. Patients in group 1 are considered to have pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah; The treatment of pulmonary hypertension due to lung disease should focus on managing the underlying lung disease and optimizing treatment of other comorbidities.3, 11 lung disease should be.
Effective therapy should be instituted in the early stages, before irreversible changes in pulmonary vasculature occur. Once the cause of group 3 pulmonary hypertension. Sotatercept for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
The two most common diseases in this group are chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis and lung diseases that lead to scarring in the lungs or pulmonary. Patients that are being screened because of high risk factors for developing pulmonary hypertension, such as patients with scleroderma or family history of pah, may rarely be diagnosed as class i. (formerly pulmonary arterial hypertension) 20 3</strong> combined postcapillary and precapillary pulmonary hypertension (ph) 15 3 isolated postcapillary ph 15 <<strong>3</strong> box 1 updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension (ph) 1.
Sotatercept for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Prognosis of group 4 pulmonary hypertension. Ad let’s build the knowledge bank to better understand, talk about, and manage rare disease.
During cardiopulmonary bypass, an organized endothelialized thrombus is dissected along the pulmonary vasculature in a procedure more complex than acute surgical embolectomy. The blood flow from the heart to the lungs is disrupted due to constricted blood vessels. Pulmonary hypertension (ph), defined as a mean pulmonary arterial pressure greater than 25 mm hg at rest or greater than 30 mm hg during exercise, is often characterized by a progressive and sustained increase in pulmonary vascular resistance that eventually may lead to right ventricular (rv) failure.
64 the clinical study to assess the efficacy and safety of macitentan in. Ordinary physical activity does not cause undue fatigue or dyspnea, chest pain, or heart syncope.

Pulmonary hypertension Respiratory Therapy Pinterest

Pin on Print Design and Layouts

Pulmonary embolism in 2020 Pulmonary embolism, Pulmonary

Chest X Rays Acute respiratory distress syndrome

Pin on Forensic pathology microscopy

Pin on Pulmonary Hypertension Awareness Month 2017

AtrialSeptal Defect (ASD). Congenital, acyanotic, heart

Pin on Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary Arterial

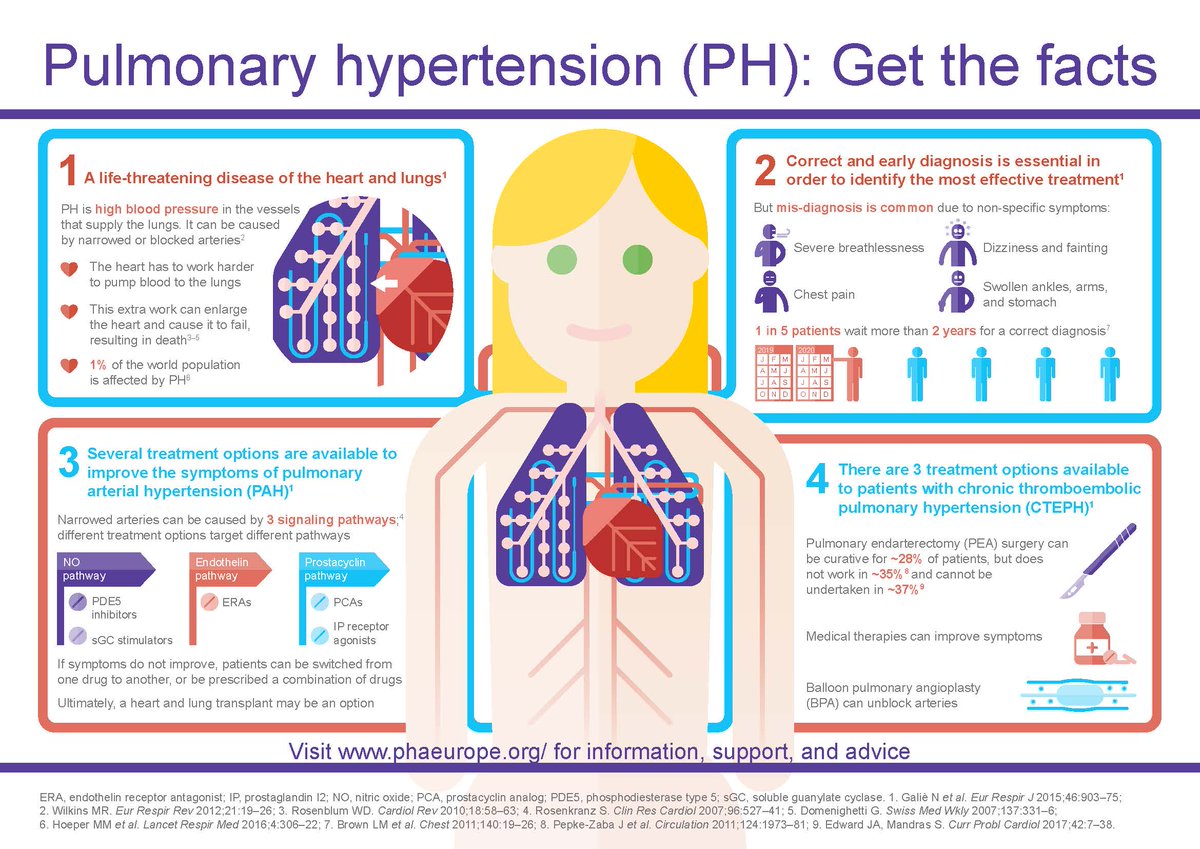









Post a Comment for "Pulmonary Hypertension Class 3 Treatment"